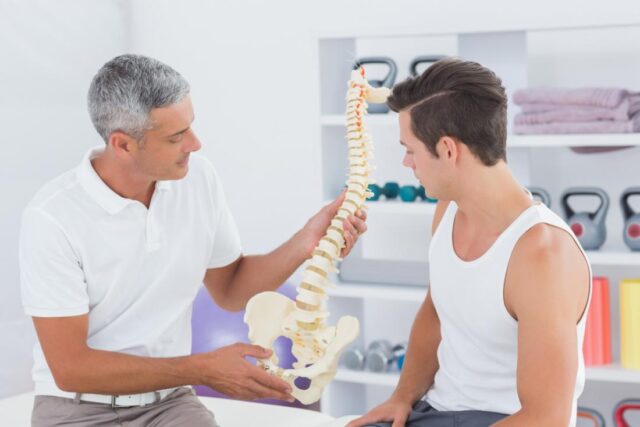

Osteopathy is a holistic approach to healthcare that emphasizes the role of the musculoskeletal system in overall health and well-being. Established in the late 19th century by Dr. Andrew Taylor Still, osteopathy initially challenged the prevailing medical practices of the time, advocating for a patient-centered approach that encourages the body’s inherent ability to heal itself.
The purpose of this blog post is to explore the role of osteopathy in modern healthcare. This exploration will span across various fields of medicine – from pain management to sports medicine, and from pediatric to geriatric care. Our journey will shed light on the rich history, principles, and educational requirements of osteopathy, and its potential for interdisciplinary collaboration.
Explaining the Principles of Osteopathy

Osteopathy revolves around three key principles. Firstly, it takes a holistic approach to healthcare, viewing the body as an interconnected system rather than a collection of individual parts. This approach acknowledges that physical ailments can significantly influence mental and emotional well-being, and vice versa.
Secondly, osteopathy emphasizes the body’s innate self-healing ability. By identifying and addressing obstacles that hinder this natural process, osteopathic physicians (also known as DOs) aim to restore and maintain optimal health.
Finally, osteopathy understands the importance of the musculoskeletal system’s impact on overall health. Any imbalance or dysfunction within this system can affect other body systems and general health, leading to a wide range of health conditions. Healthcare providers such as Osteopaatti Helsinki could also confirm everything we wrote above and below in the article.
Education and Training of Osteopathic Physicians
Osteopathic and allopathic (MD) training follow similar paths, including pre-medical education, four years of medical school, and residency programs. However, DOs receive additional training in osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT), a hands-on technique used to diagnose, treat, and prevent illness or injury.
This training integrates traditional medical practices with osteopathic principles, cultivating a comprehensive understanding of how changes in the musculoskeletal system can affect other body systems. By incorporating OMT, osteopathic physicians can address a variety of health conditions from a holistic perspective.
Scope of Practice for Osteopathic Physicians

DOs often serve in primary care roles, providing comprehensive patient care while focusing on preventive health. They are licensed to diagnose and treat illnesses, prescribe medication, and perform surgery.
In addition to these conventional practices, DOs utilize OMT to complement standard treatment approaches. They frequently collaborate with other healthcare professionals, showcasing osteopathy’s flexibility and its potential for interdisciplinary integration within the healthcare system.
Conditions Treated by Osteopathy
Osteopathy treats a broad spectrum of conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders, chronic pain, and systemic conditions like digestive disorders. By using OMT, which involves gentle manual techniques, osteopathic physicians can effectively address issues such as back pain, neck pain, headaches, and joint pain that may result from imbalances or dysfunctions within the body’s musculoskeletal system.
In chronic pain management, osteopathy offers an alternative or adjunct to traditional pharmacological interventions, which can often have undesirable side effects or limited effectiveness. Through techniques like soft tissue manipulation, osteopathic physicians can help patients manage their pain more effectively by addressing the root causes of their discomfort, promoting improved blood circulation, relieving muscle tension, and enhancing the body’s self-healing mechanisms.
This holistic approach to pain management can provide patients with long-lasting relief and a reduced reliance on medication, empowering them to regain control over their physical well-being.
Osteopathy in Pain Management
Osteopathy’s holistic approach shines in pain management, often tackling pain sources rather than symptoms. This non-pharmacological approach to pain relief makes osteopathy an appealing choice for those struggling with chronic pain conditions. Unlike traditional pharmaceutical interventions that may only provide temporary relief, osteopathic physicians delve deeper to identify and treat the underlying causes of pain, taking into account the interconnectedness of the body’s systems.
OMT techniques, like soft tissue manipulation and joint mobilization, directly address pain’s physical dimensions. By applying gentle pressure, stretching, and manipulating specific areas of the body, osteopathic physicians can correct structural imbalances, improve circulation, and promote flexibility.
These targeted interventions not only alleviate pain but also aim to restore functionality, allowing individuals to regain their independence and engage in activities they may have had to give up due to pain.
Additionally, by addressing the root causes of pain, osteopathy can help prevent further complications and reduce the reliance on pain medications, contributing to a more sustainable and comprehensive approach to pain management.
Osteopathy in Sports Medicine
In the realm of sports medicine, osteopathy plays a significant role in rehabilitation, injury prevention, and performance enhancement. Athletes often face musculoskeletal misalignments and imbalances due to the nature of their activities.
Osteopathic physicians work closely with athletes and their trainers to maintain optimal musculoskeletal health, reducing the risk of injury and enhancing athletic performance. OMT techniques can help correct these imbalances, improve muscle function, and boost overall performance.
Osteopathy in Pediatric Care
For infants and children, osteopathy offers gentle, non-invasive treatment options. Conditions like infant colic, sleep disorders, and even certain behavioral issues can be addressed through osteopathy.
By promoting optimal growth and development, osteopathic care can help set a solid foundation for a child’s overall health, potentially reducing future health complications.
Osteopathy in Geriatric Car
Osteopathy’s role in geriatric care revolves around addressing age-related musculoskeletal issues, improving mobility and balance, and enhancing seniors’ overall quality of life. With gentle, non-invasive techniques, osteopathic care can help manage conditions like arthritis, postural problems, and chronic pain, often associated with aging.
Osteopathy and Mental Health
By incorporating OMT techniques, such as gentle manipulations, myofascial release, and craniosacral therapy, osteopathy aims to address the physical manifestations of mental health issues. These techniques help release muscle tension, enhance blood circulation, and stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to a sense of calm and relaxation.
Moreover, by improving overall physiological functions, osteopathy contributes to a healthier body-mind balance, enhancing the individual’s resilience to stressors. This holistic approach highlights the importance of integrating comprehensive mental health care within the broader medical field, recognizing that mental and physical well-being are intricately intertwined.
Research and Evidence Supporting Osteopathy

While osteopathy’s efficacy is widely accepted within the profession, research validation is an ongoing process. Numerous studies have demonstrated OMT’s effectiveness in treating conditions like low back pain and tension headaches.
However, challenges exist in producing comprehensive research due to osteopathy’s individualized approach to patient care. Despite these challenges, the profession continues to contribute valuable insights to medical research, further cementing its place in modern healthcare.
Conclusion
The role of osteopathy in healthcare is multifaceted, encompassing various fields of medicine. Its holistic, patient-centered approach offers valuable insights and potential for interdisciplinary collaboration.
Whether you are a patient exploring treatment options, a healthcare professional interested in comprehensive care, or simply a curious reader, osteopathy’s holistic and integrative approach to health and wellness is worth considering. It offers a unique perspective on health and well-being, emphasizing the body’s inherent ability to heal and the importance of the musculoskeletal system in overall health.









