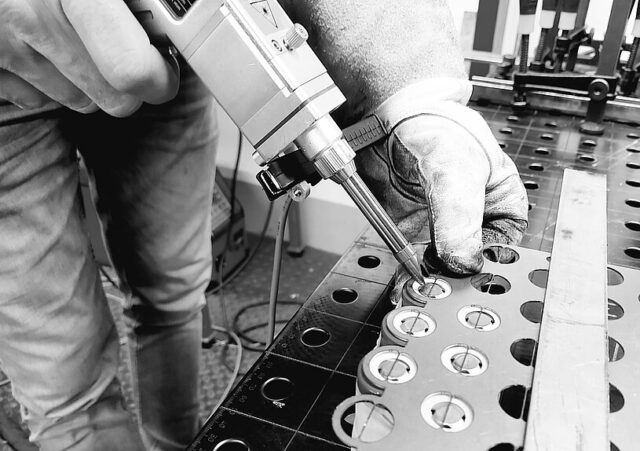
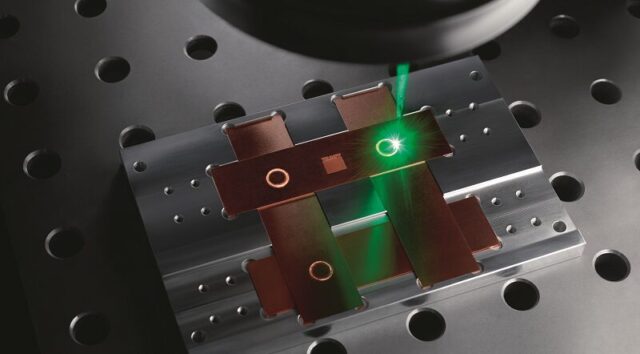
Battery laser welding is not just a technological marvel; it’s a testament to human ingenuity in our quest for manufacturing perfection. By offering a precise and efficient way of melding materials, this technology is steadily transforming the manufacturing world. Our modern landscape, burgeoning with portable electronic devices and a rapidly evolving electric automotive sector, demands innovations that keep pace. Here, battery laser welding stands tall as the answer, ensuring both longevity and top-tier functionality for the diverse range of products integral to our daily lives.
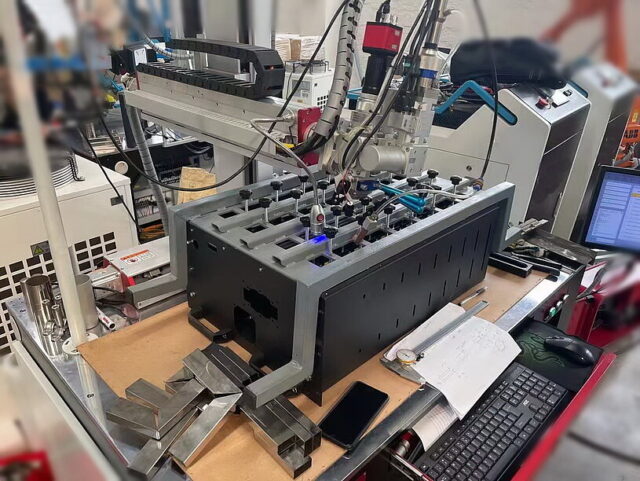

Understanding Battery Laser Welding
Diving deep into its mechanics, battery laser welding employs a concentrated beam of light to melt and subsequently join materials. This energy, focused and unyielding, can be expertly maneuvered to craft fine, accurate welds. It’s a finesse game, making it the gold standard for delicate operations — be it welding the wafer-thin sheets of metal in intricate designs or piecing together the complex components of electronics. The automotive and electronics sectors, in particular, owe much of their advancements to this method. Consider the minuscule joints in your smartphone battery or the complex connections nestled within an electric vehicle’s battery pack. Battery laser welding has seamlessly integrated itself, proving indispensable in producing such high-precision work.
Advantages of Battery Laser Welding
When dissecting its allure, several advantages of the battery laser welding machine come to the fore. First and foremost, the precision: The laser’s inherent ability to target minuscule, specific areas without inadvertently affecting or damaging surrounding materials is unparalleled. Next, there’s efficiency: In a world driven by timelines, laser welding’s rapid operations significantly truncate manufacturing times, making it an industry favorite. But the jewel in its crown is the Minimal Heat-Affected Zones (HAZ): Due to the technology’s localized heating, there’s minimal thermal distortion, which in turn guarantees that components in close proximity remain unscathed.
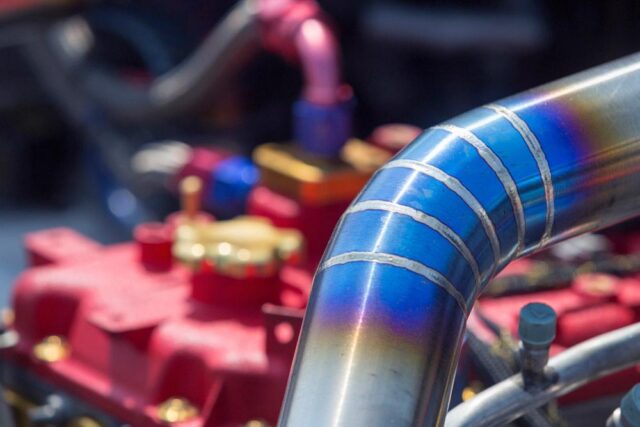

Selecting the Right Equipment
While understanding the theory is vital, practical implementation demands a keen eye for equipment. Your results hinge on your tools. When on the hunt for a laser welding system, several factors demand attention. Power tops the list, ensuring your welds achieve the necessary depth and hold. Then there’s Wavelength: It’s a nuanced game as different materials have varying affinities for absorbing specific wavelengths. Lastly, Pulse Duration enters the fray. While short pulses are adept at curtailing HAZ, longer pulses often pave the way for deeper, more robust welds.
Safety Precautions
Navigating the world of laser welding requires more than expertise; it demands a commitment to safety. The powerful beams, while instrumental in achieving precise welds, can also be hazardous. It’s paramount to wear Protective Gear, including laser-safe goggles that specifically block the laser’s wavelength, ensuring that workers’ eyes are shielded from potential harm. Next, a Proper Workspace Setup is non-negotiable. This involves a well-ventilated space, barriers or curtains to contain the laser beam, and clearly marked hazard zones. Regular training sessions should underscore the importance of safety protocols, ensuring everyone remains vigilant and informed.
Material Selection
A craftsman is only as good as their materials. And in the realm of battery laser welding, material selection can make or break the outcome. The Thickness of the material often dictates the type of laser and its parameters. Thinner materials typically require lasers with shorter pulse durations to prevent burn-through, while thicker materials might need more powerful lasers. Compatibility is another significant consideration. Not all materials take well to laser welding, and some combinations can lead to brittle welds. Research and pre-testing become pivotal, ensuring the chosen materials meld seamlessly and maintain structural integrity post-welding.
Optimizing Welding Parameters
Crafting the perfect weld is akin to fine-tuning a musical instrument. Several parameters need meticulous adjustments to produce harmony. Pulse Frequency determines how often the laser fires; a higher frequency can lead to smoother welds but also increased heat input. Power Density impacts how much energy the material absorbs; it must be optimized to ensure full penetration without causing damage. Spot Size is another contender. While smaller spots provide more concentrated energy and precision, they can increase the risk of burn-through on thinner materials. Balancing these elements is an art, demanding both knowledge and experience.
Preparation and Cleaning
An oft-overlooked yet crucial step is the preparation and cleaning of materials. Any contaminants, be they oils, oxides, or residues, can drastically compromise weld quality. A clean surface ensures that the laser’s energy is efficiently used for welding, rather than burning off impurities. Methods like ultrasonic cleaning, chemical etching, or simple isopropyl alcohol wipes can be employed, depending on the material and contamination level. This meticulousness guarantees a more consistent and high-quality weld.
Techniques for Precision Welding
Precision is the lifeblood of battery laser welding. Enhancing accuracy often involves the strategic use of Fixtures and Jigs. These tools ensure materials are held steady, minimizing movement during the welding process. Additionally, embracing Automation can exponentially increase precision, especially for repetitive tasks. Computer-controlled laser systems can replicate intricate weld patterns with unparalleled accuracy, ensuring consistency across large batches.
Monitoring and Quality Control
Real-time monitoring is the guardian angel of laser welding. With advancements in technology, systems now offer instantaneous feedback, flagging any deviations or potential issues. Coupled with post-weld inspections using techniques like ultrasonic testing or X-ray imaging, manufacturers can ensure every weld meets the highest standards. This vigilance not only guarantees product quality but also fosters trust among consumers and stakeholders.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
No process is without its challenges, and battery laser welding is no exception. Porosity, the formation of gas pockets in welds, can be countered by optimizing shielding gas flow or adjusting laser parameters. Spattering, where molten material is ejected from the weld area, can be mitigated by tweaking the pulse frequency or power density. Recognizing these issues and understanding their solutions ensures smoother operations and superior end products.
Conclusion
Battery laser welding is a symphony of science, art, and technique. Its mastery lies in understanding its nuances, respecting its power, and continually striving for precision and efficiency. As industries evolve and technologies advance, this form of welding will undoubtedly remain pivotal. Embrace these insights, apply them to your projects, and witness the transformative power of precision and efficiency in action.